Data management challenges more common than ever before
The complexity of data management in today's manufacturing enterprise presents a myriad of challenges that are more prevalent than ever before. Manufacturers grapple with issues like:
- Data fragmentation across disparate systems
- Silos that hinder accessibility and visibility
- Difficult to adopt or scale new applications
- Performance issues with low/slow data velocity
- Expensive to manage and maintain
The sheer volume of data generated by modern manufacturing processes can overwhelm traditional data management systems, making it difficult to extract meaningful insights.
Additionally, the integration of new technologies like IoT devices adds another layer of complexity, requiring a robust platform that can handle vast streams of real-time data.
Ensuring data quality and consistency across the board remains a formidable task, as does complying with ever-evolving regulatory requirements and protecting sensitive information against cyber threats. These obstacles underscore the necessity for a strategic approach to data management that embraces innovative solutions and best practices, paving the way for optimized operations and informed decision-making in the manufacturing sector.
Use data to fuel systems, performance, and programs
Harness the full potential of your data to give your company a competitive edge. Make more use of the data your systems already have. Capture even more data from machines and equipment. What else can your company do with data?
- Feed other systems and platforms to compound the value of IT and system investments
- Capture more data from machines and equipment to feed manufacturing execution system (MES), manufacturing operations management (MOM), or OEE system
- Drive even more value with your company’s ERP using shop floor data from the MES, MOM, or OEE system
- Fuel the company’s continuous improvement program with OEE data
Your company may already have access to real-time data from sensors and connected devices. Put the data to work to inform business-critical decisions for customer service, inventory, maintenance, and operations management.
Modern data architectures accelerate digital transformation and reduce maintenance costs
Reducing or eliminating point-to-point integrations can have a profound impact on new technology adoption.
Legacy integration techniques rely heavily on system-to-system extract, transform, load (ETL) systems. It's an approach that creates a complex architecture that's difficult for systems users to understand, and expensive for companies to support. Beyond system implementation cost and complexity, applications with multiple integrations are expensive to replace and decommission. The result is using older technology for much longer than the business value justifies.
A modern data management strategy and architecture streamlines new technology implementation and reduces technical debt associated with a traditional ETL approach.
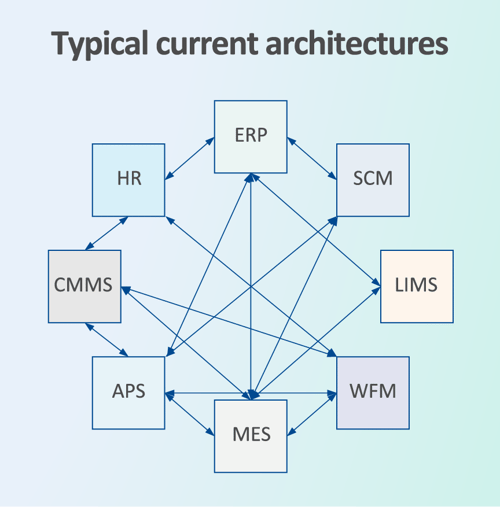
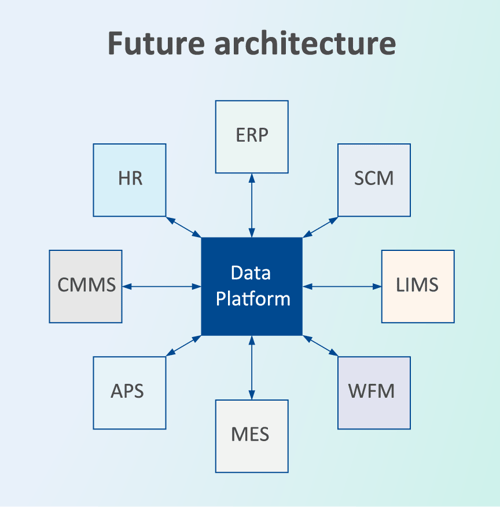
Exploring options for effective data management architecture
Which data management approach and architecture works best for supply chain and the manufacturing enterprise?
Choosing the right approach and architecture for data management in manufacturing and the supply chain is critical for achieving operational efficiency and strategic agility. Hub-and-spoke emerges as the favored approach, blending the strengths of traditional databases, data warehouses, and the latest in cloud storage and computing technologies, with solutions that make data FAIR — findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable.
Adopting a FAIR data approach serves as the linchpin for harnessing the full potential your company's data assets. This methodology aligns with the evolving needs of modern manufacturing and supply chain operations and addresses the myriad of challenges these sectors face. By ensuring that data adheres to these principles, businesses can create a more integrated, efficient, and flexible data architecture. FAIR data eliminates data silos and enables data sharing and collaboration, enabling front-line workers and stakeholders to derive meaningful insights swiftly and make decisions with greater confidence. FAIR data principles act as a catalyst for innovation, propelling manufacturing and supply chain enterprises toward a future where data-driven decision-making is the norm, not the exception. As companies transition towards this robust data management architecture, they set the stage for leveraging advanced analytics and AI, thereby achieving operational excellence and maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly data-centric world.
Understanding key features of a FAIR data system for manufacturing companies

To meet the specific needs of manufacturing companies, a FAIR data system must embody several key features that directly address the unique challenges faced by the sector. A robust FAIR data solution should offer seamless data discovery and efficient management tools that ensure data is easily findable and accessible, regardless of its source.
Interoperability is another critical component, as it allows data from diverse systems and technologies within the manufacturing process to be integrated and analyzed cohesively. Furthermore, the system must support data re-usability, empowering companies to leverage historical data for predictive analytics, trend analysis, and strategic planning.
By incorporating advanced security measures and compliance protocols, the FAIR data solution not only enhances operational efficiency but also safeguards sensitive information against cyber threats and ensures adherence to regulatory standards. With these capabilities, manufacturing companies can unlock the full potential of their data assets, fostering innovation, optimizing production processes, and maintaining a competitive edge in the fast-paced industrial landscape.
Transitioning into the steps for implementing such a data management system requires a strategic approach that encompasses data security and compliance, underlining the importance of protecting the integrity and confidentiality of manufacturing data in today's digital age.
Key feature: Data security and compliance in manufacturing
Data security and regulatory compliance are bedrocks for implementing a FAIR data solution, underscoring the importance of protecting not just the integrity and confidentiality of data but also ensuring the sustainable and ethical use of information. As a manufacturing enterprise navigates digital transformation, adhering to security standards and regulatory frameworks is absolutely critical. This is because, in an era where data breaches and cyber threats are rampant, the repercussions of compromised data can be catastrophic, not only in terms of financial losses but also in reputational damage and operational disruptions. Moreover, compliance with regulations ensures that manufacturing companies can operate within legal boundaries, avoiding hefty fines and sanctions that could derail their operations. Thus, a strategic focus on data security and compliance within the FAIR data framework is not merely a defensive measure but a proactive strategy that safeguards the company’s assets, fosters trust among stakeholders, and lays a strong foundation for leveraging data analytics to fuel business growth and innovation. This strategic approach to data management, focusing on security and compliance, seamlessly transitions into exploring the risks associated with data security breaches in manufacturing and how to mitigate them, underpinning the necessity of robust data security measures and strict adherence to regulatory requirements in today's data-driven manufacturing landscape.
Key feature: Data accuracy and integrity in manufacturing
In the intricate ecosystem of supply chain and manufacturing, the importance of maintaining high-quality data cannot be overstated. High-quality data is the foundation of operational efficiency efforts, enabling manufacturers to make precise decisions, optimize production processes, and elevate product quality. To ensure data accuracy and integrity, it is imperative to implement rigorous data quality control measures. This involves establishing standardized data collection processes, employing advanced data validation and cleansing tools, and fostering a culture where data accuracy is prioritized at every level of the organization. By making data quality essential for operations excellence, manufacturers can safeguard against the costly repercussions of inaccurate data, such as production errors, supply chain disruptions, and flawed decision-making. As a company transitions towards a more data-driven manufacturing environment, the role of data governance becomes increasingly pivotal, ensuring that the data not only remains of high quality but is also managed and utilized in a way that aligns with the strategic goals of the organization.